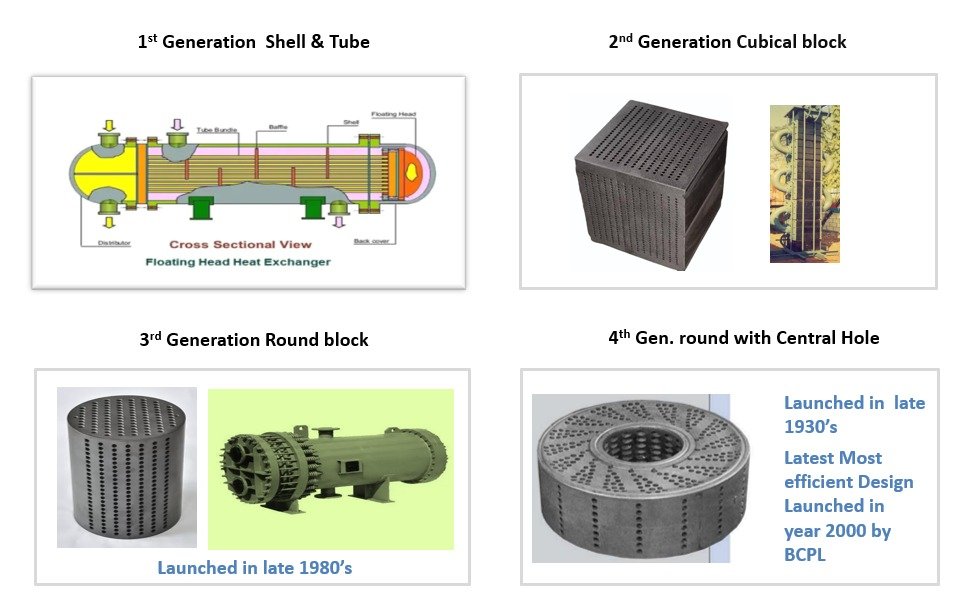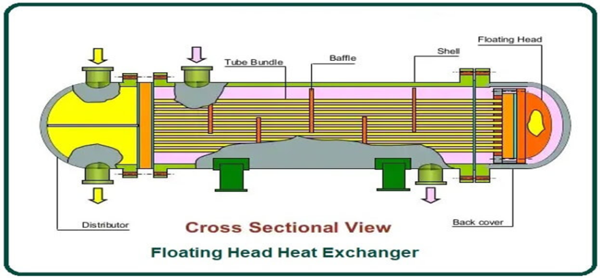
1st Generation Shell & Tube type was introduced around the year 1900
- Limitations....
- Gr Tubes & tube sheets are joined by cementing, after some period of thermal cycles cement starts to cracks resulting in leakages.
- L/D ratio in shell & tube Hx is very high due to long tube length. This develop laminar flow the pattern causing serious fouling and depositions, which chokes the tubes.
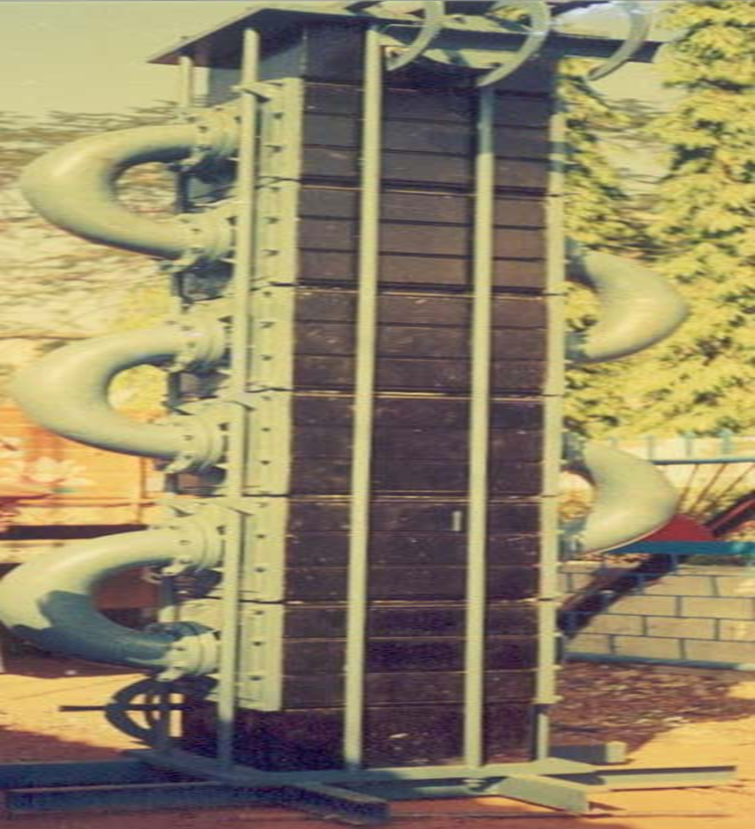
2nd Generation Cubical block type was introduced around the year 1930's
- Limitations....
- Any leakage from the process side will result in the direct spillage of hazardous chemicals in the plant area, raising various safety issues.
- 6 tie rods are used to hold and maintain pressure in each graphite block. These tie rods many times gets rust & develops cracks on sides of the blocks.




3rd Generation Design with Circular blocks of Graphite Shelled in metal sheets was introd- uced around the year 1980's
- Limitations....
- This design suffered from unequal flow & created hot spots/ uneven thermal distribution and higher fouling & deposits in central utility channels along diameter due to longer channel lengths.
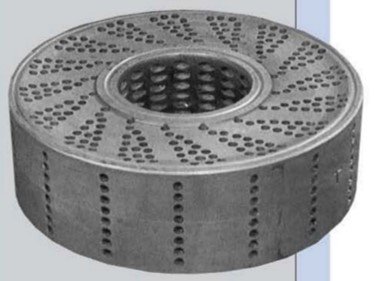
4th Generation equal tube length in the process side & service side and Heat transfer area design with central hole in the graphite element introd- uced in the Beginning of the year 2000, 21¹¹ Century, by BCPL.
- Limitations....
- This central hole design creates high turbulence which improves heat transfer efficiency and cuts down the risk of fouling or deposits.
- This 4th Generation, the L/D ratio of the holes is very small to prevent a steady flow rate being established before the fluid reaches the outlets; and this increases the heat transfer coefficient.